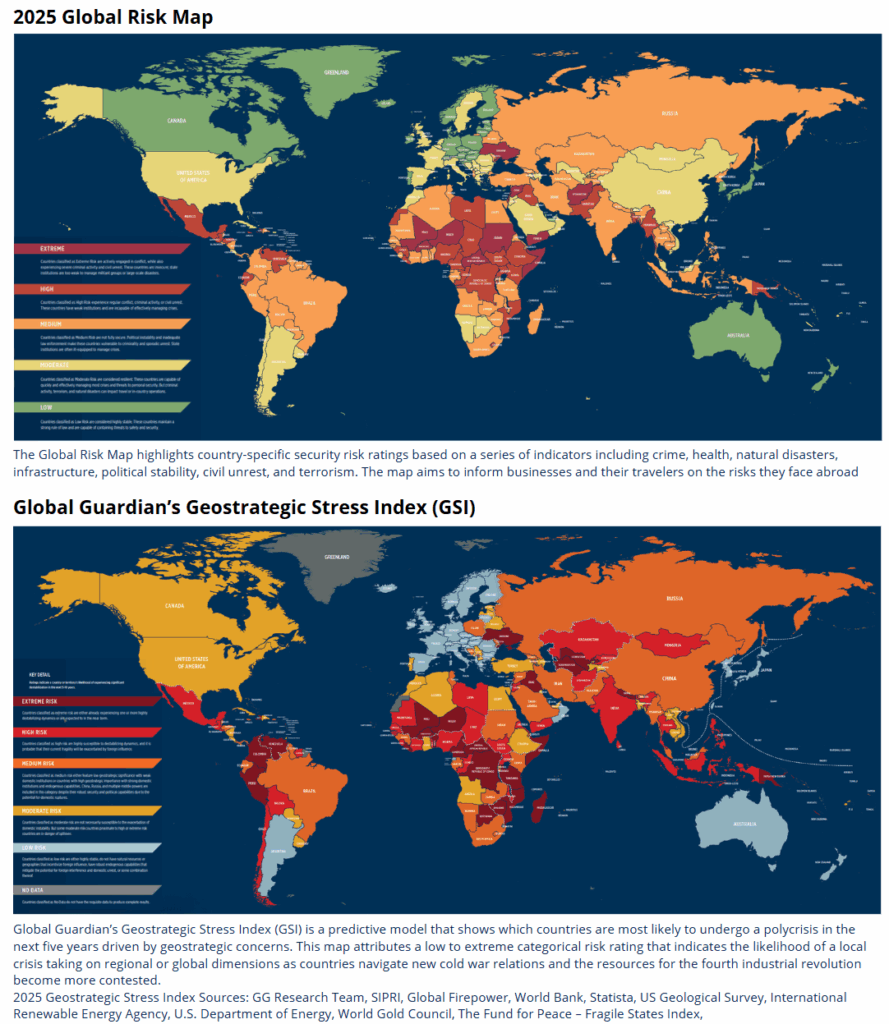
Geopolitical risks are reshaping investment strategies in 2025, with global trade protectionism, regional conflicts, and political instability fuelling both volatility and opportunity. Heightened tariffs and trade barriers—especially between the U.S. and China—are disrupting global supply chains, while ongoing wars in Ukraine, the Middle East, and the Asia-Pacific have understandably given investor to be nervous.
Top Risks Identified: the following as the most significant geopolitical risks currently:
- Global Trade Protectionism: Escalating tariffs and trade barriers, particularly between the U.S., China, and other major economies, threaten global supply chains and increase economic uncertainty.
- Middle East Regional War: Ongoing and potential escalation of conflict in the Middle East, especially involving Israel, Iran, and neighboring states, with risks of regional spillover.
- U.S.-China Strategic Competition: Heightened rivalry over trade, technology, and security, especially regarding Taiwan and the South China Sea.
- Global Technology Decoupling: Moves by the U.S. and China to separate their technology sectors, affecting global tech supply chains and investment flows.
- Major Cyber Attacks: Rising frequency and severity of cyber incidents targeting critical infrastructure and financial systems.
- Major Terror Attacks: Increased risk of large-scale terrorist incidents, particularly in Europe and Asia.
- Russia-NATO Conflict: Ongoing war in Ukraine and heightened tensions between Russia and NATO, with risk of direct confrontation.
- Emerging Markets Political Crisis: Political instability in key emerging economies, especially in Latin America and Africa, impacting local and global markets.
- North Korea Conflict: Escalating tensions on the Korean Peninsula, with risks of military confrontation.
European Fragmentation: Political and economic divisions within the EU, including risks around fiscal policy, migration, and populist movements
Key Catalysts for Increased Defense Spending
- Heightened Geopolitical Tensions: Ongoing conflicts such as the Russia-Ukraine war, escalating tensions in the Middle East, and strategic competition between the U.S. and China are major drivers of global military expenditure.
- NATO and U.S. Policy Shifts: Pressure from the U.S., particularly under potential Trump administration policies, for European NATO members to increase their defense spending has led to significant budget hikes across Europe, with some countries aiming for 2.5–5% of GDP devoted to defense.
- Technological Advancements: Investments in AI, cybersecurity, drones, and other advanced technologies are central to modern defense strategies, further boosting spending.
- Regional Arms Races: Countries in Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, India, Taiwan) are rapidly increasing military budgets in response to unresolved disputes and mounting regional tensions.
- Supply Chain and Economic Security: Governments are prioritizing the protection of critical infrastructure and supply chains, especially for minerals and metals essential to defense industries.
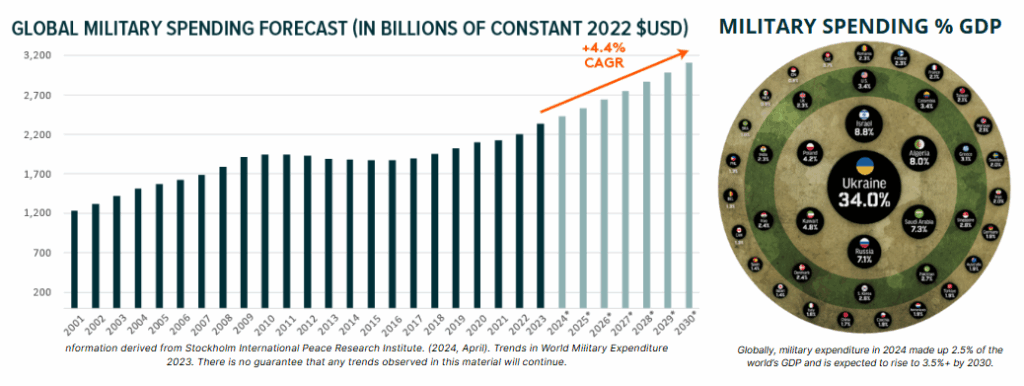
Global defense spending is increasing
Governments worldwide are prioritizing national security and modernizing defense capabilities, with NATO countries under particular pressure to increase defense budgets—potentially to as high as 5% of GDP—which would further bolster revenues for defense contractors.
While risks such as supply chain fragmentation, policy uncertainty, and market volatility persist, defense firms are well-positioned to benefit from sustained increases in government outlays, technological innovation, and heightened demand for advanced systems, making the sector a defensive play in an increasingly uncertain global landscape.
Defense stocks are set to benefit due to the unprecedented rise in global military spending, driven by escalating geopolitical tensions, persistent conflict in Ukraine, heightened U.S.-China rivalry, and ongoing instability in the Middle East.
Defense companies that benefit from general Geopolitical turmoil & NATO de-funding
The overlap between the defense companies poised to benefit from increased global defense spending (due to conflicts in Ukraine, the Middle East, Taiwan Strait, etc.) and those that would gain from NATO members increasing their own defense spending is significant. Both scenarios favor large, diversified defense contractors with strong international sales and advanced military technology offerings.
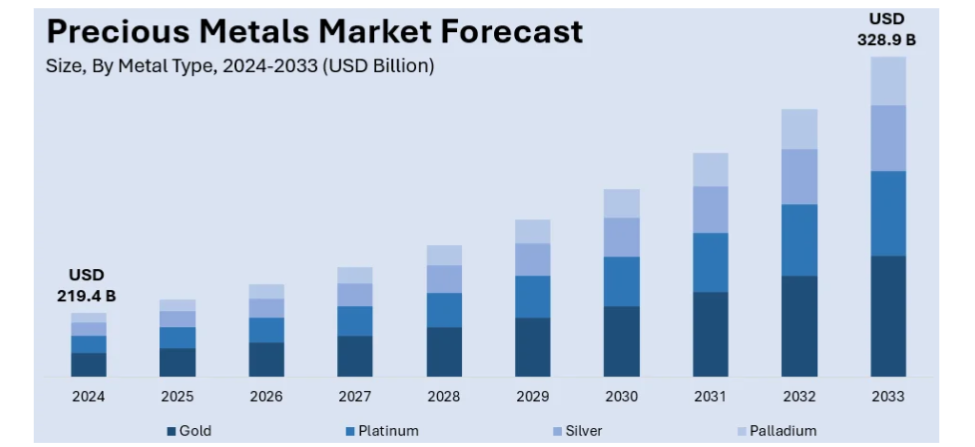
Key Catalysts for the Rise of Silver and Platinum
- Geopolitical Instability in Producing Nations: The majority of silver and platinum production comes from politically unstable countries (e.g., South Africa, Zimbabwe, Russia for platinum; Mexico, Peru, Bolivia for silver), where political crises, resource nationalism, and regulatory changes disrupt supply.
- Trade Protectionism and Sanctions: Escalating tariffs, trade barriers, and sanctions (e.g., U.S.-China trade tensions, sanctions on Russia) fragment supply chains and restrict the flow of metals, leading to supply shortages and price volatility.
- Resource Nationalism: Governments in key producing countries are increasing taxes, tightening regulations, and sometimes threatening nationalization, deterring investment and creating uncertainty for mining operations.
- Supply Chain Fragmentation: Efforts by nations to secure critical minerals and reduce dependence on geopolitical rivals are leading to a patchwork of bilateral deals, export restrictions, and stockpiling, further straining supply.
- Safe-Haven Demand: During periods of heightened geopolitical risk, investors turn to precious metals like silver and platinum as hedges against uncertainty, driving up prices.
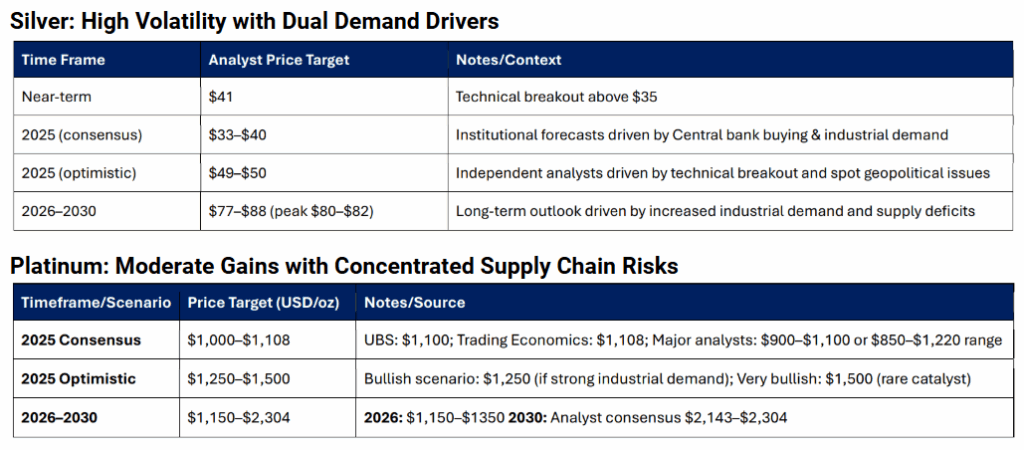
Platinum: Moderate Gains with Concentrated Supply Chain Risks
In 2025, platinum is experiencing moderate price gains, largely driven by a surge in investment demand amid tariff uncertainties and strong Chinese buying. Supply remains tight, marking the third consecutive annual deficit due to significant production cuts in South Africa and Zimbabwe. These supply constraints are further exacerbated by weak recycling rates and a shortage of end-of-life catalytic converters.
Geopolitical risks add to the market’s fragility. South Africa faces political tensions with the US over AGOA trade threats and internal governance issues, while Zimbabwe’s civil unrest and Russia’s sanctions continue to threaten supply stability. Additionally, platinum’s critical use in catalytic converters exposes it to energy market shocks, especially from potential Middle East conflicts. Overall, while moderate gains are possible, platinum’s outlook is clouded by concentrated and persistent supply chain risks.
Got a question about this article? Ask the Team at MPC
ASK A QUESTION

GENERAL ADVICE WARNING:
Recommendations and reports managed and presented by MPC Markets Pty Ltd (ABN 33 668 234 562), as a Corporate Authorised Representative of LeMessurier Securities Pty Ltd (ABN 43 111 931 849) (LemSec), holder of Australian Financial Services Licence No. 296877, offers insights and analyses formulated in good faith and
Opinions and recommendations made by MPC Markets are GENERAL ADVICE ONLY and DO NOT TAKE INTO ACCOUNT YOUR PERSONAL CIRCUMSTANCES, always consult a financial professional before making any decisions.

